1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| """
This part of code is the Q learning brain, which is a brain of the agent.
All decisions are made in here.
View more on my tutorial page: https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/
"""
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
np.random.seed(2)
class QLearningTable:
def __init__(self, actions, learning_rate=0.01, reward_decay=0.9, e_greedy=0.9):
self.actions = actions
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.epsilon = e_greedy
self.q_table = pd.DataFrame(columns=self.actions, dtype=np.float64)
def choose_action(self, observation):
self.check_state_exist(observation)
if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon:
state_action = self.q_table.loc[observation, :]
action = np.random.choice(state_action[state_action == np.max(state_action)].index)
else:
action = np.random.choice(self.actions)
return action
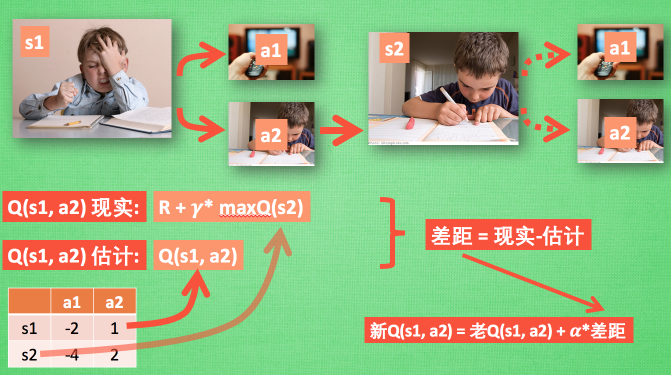
def learn(self, s, a, r, s_):
self.check_state_exist(s_)
q_predict = self.q_table.loc[s, a]
if s_ != 'terminal':
q_target = r + self.gamma * self.q_table.loc[s_, :].max()
else:
q_target = r
self.q_table.loc[s, a] += self.lr * (q_target - q_predict)
def check_state_exist(self, state):
if state not in self.q_table.index:
self.q_table = self.q_table.append(
pd.Series(
[0]*len(self.actions),
index=self.q_table.columns,
name=state,
)
)
|